In this article, we are going to discuss the properties of matter, so let’s get started…
What is matter?
Before we start our discussion on the properties of matter, it is good for us that first, we understood the term matter. So what is the matter?
| Definition of the matter: Anything in our surroundings that have mass and occupy space by its volume is called matter. |
Everything that you see in your surroundings is matters because they have mass and have volume and must occupy some space. Matter exists in our surroundings in three forms or states i.e solids, liquids, and gases.

Suggested reading: matter, nature of matter and its classification
Properties of matter
So there are three states of matter that is solid, liquids, and gases. These three states of matter have their own unique or characteristic properties that make them different from each other.
A matter can be seen both as a chemical and physical entity. At the microscopic level such as molecular, atomic, and sub-atomic level, we deal with its chemical behavior. But at the macroscopic level, we deal with is physical behavior of the matter.
Any characteristic that can be measured, such as an object’s density, color, mass, volume, length, malleability, melting point, boiling point, hardness, odor, pressure, temperature, electrical conductivity, reactivity, toxicity, flammability, acidity, basicity, oxidation, reduction, combustion and more, are considered properties of matter.
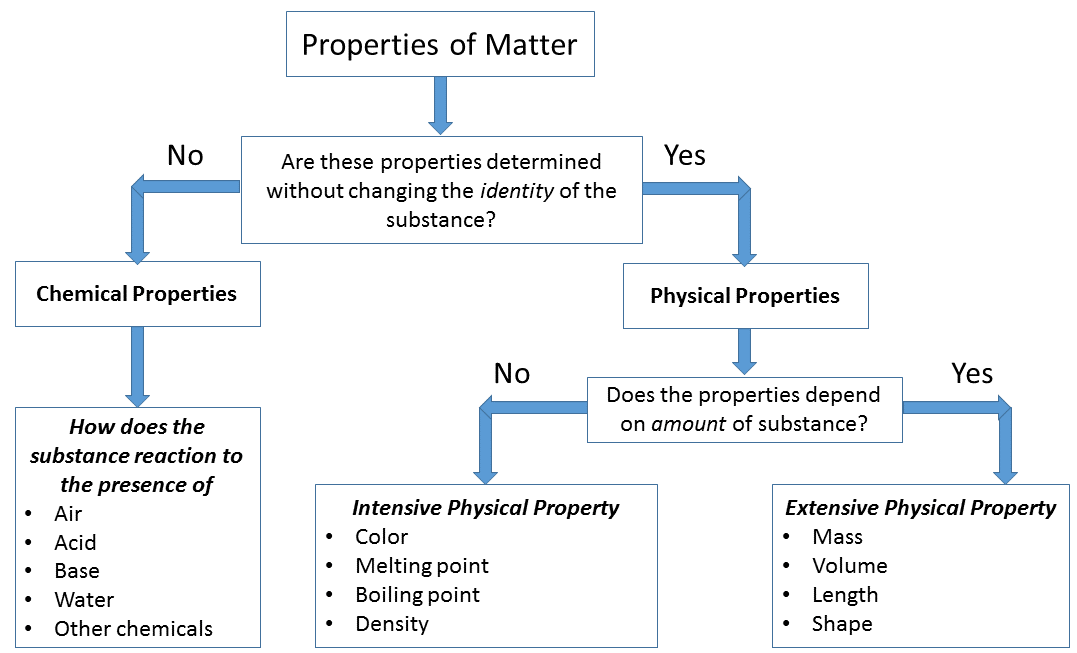
Properties of a matter can be classified in two groups on the basis of changing of the identity or composition of the matter, such as-
- Physical properties of matter
- Chemical properties of matter
Physical properties of matter
Physical properties are those properties of matter that can be measured or observed without changing the identity or composition of the substance.
- All matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms, and each atom have mass and have some volumes. When atoms combines, it forms molecules and when molecules combines, it forms observable matter such as solid and liquid and can form unobservable matter such as gases, that contains the properties of mass and volume.
- Physical properties of matter are attributed to those matter which is independent of chemical composition.
- Mass, volume, length, shape, density, colour, hardness, melting, boiling points, temperature, pressure, electrical conductivity, and thermal conductivity are all examples of physical properties.
All matters have either physical or chemical properties and all physical properties are either intensive or extensive. So physical properties of matter are further divided into two types i.e
- Intensive physical properties of matter
- Extensive physical properties of matter
Intensive physical properties of matter
Intensive properties of matter – It is a characteristic property of matter that does not depend on the amount of matter being measured, such as density, colour etc.
So intensive property of a matter is a physical quantity that does not depend on the amount of matter which is being measured. For example, temperature is an intensive property of matter. In the thermal equilibrium of a system, the temperature will be the same at every part of the system. If we make a wall and create a partition between the system such that it is permeable for matter and heat then every partition of the system has an identical temperature.
But If a system is divided by a wall that is impermeable to heat and to matter, then each subsystem or partition can have different temperatures. It is the same for the density if the system is homogenous.
Some intensive physical properties of matter are:
- Colour
- Density
- Melting point
- Boiling point
- Thermal conductivity
- Temperature
- Pressure
These physical properties of matter are independent of the amount of matter being measured.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/intensive-vs-extensive-properties-604133-v3-5b55fb394cedfd0037117796.png)
Extensive physical properties of matter
Extensive properties of matter – It is characteristic property of matter that depends on the amount of matter being measured, such as mass and volume. It directly depends on the amount of matter being measured.
So extensive properties of matter are a physical quantity that depends on the amount of matter which is being measured. In other words, the extensive property is a physical quantity whose value is proportional to the size of the system. For example, mass is an extensive property of matter. If you take a system in which mass is uniformly distributed and if you half the system then the mass of both parts will be reduced to half. This is also the same for the volume. So mass and volume like quantity depend on the amount of matter taken.
Some extensive physical properties of matter are:
- Mass
- Volume
- Amount of substance
- Enthalpy
- Electrical conductivity
- Length
- Shape and size
Chemical properties of matter
Chemical properties of matter are those properties of matter that can be measured or observed with the changing of the identity or composition of the substance.
In other words, it is the characteristic property of the matter that can be determined only by changing a substance’s molecular structure.
At the atomic or molecular level when atoms and molecules of different elements react to each other then the reactant undergoes different and unique atomic arrangements and electronic configuration so as they give a new product. This type of property is only determined by changing a substance’s molecular structure.
- Chemical properties of matter is attributed to those matter whose measurements is dependent on the chemical composition.
- Flammability, toxicity, acidity, reactivity of different types, and heat of combustion are examples of chemical properties.

Several examples of chemical properties are given below:
- When a compound undergoes complete combustion (burning) with oxygen, then the energy released in this process is called heat of combustion. The symbol for the heat of combustion is ΔHc.
- Chemical stability – It means, whether a compound will react with water or air (chemically stable substances will not react). So hydrolysis and oxidation are two such reactions and are both chemical changes.
- Reactivity – It is a tendency of matter to combine chemically with other substances. Some materials are highly reactive, whereas others are extremely inactive and do not react. For example, Potassium is extremely reactive, even in the presence of water. A pea-sized piece of potassium can reacts explosively when combined with a small volume of water.
- Flammability – It is the tendency of the matter to burn. When matter burns in presence of oxygen, it reacts with oxygen and transforms into various substances. Dry wood is an suitable example of flammable material.
- Toxicity – It refers to the extent to which a chemical element or a combination of chemicals may harm an organism.
- Redox or oxidation-reduction reaction – It is a type of reaction in which the oxidation number of a molecule, atom, or ion is changes by gaining or losing an electron. Redox reactions are common and vitally used in some of the basic functions of life, such as photosynthesis, respiration, combustion, and corrosion or rusting.
The chemical properties of matter become very useful when we want to distinguish between the two different chemicals or to study the different chemical compounds. Chemical properties of matter can only be seen when materials are in the process of being changed to another new substance.
Stay tuned with Laws Of Nature for more useful and interesting content.



